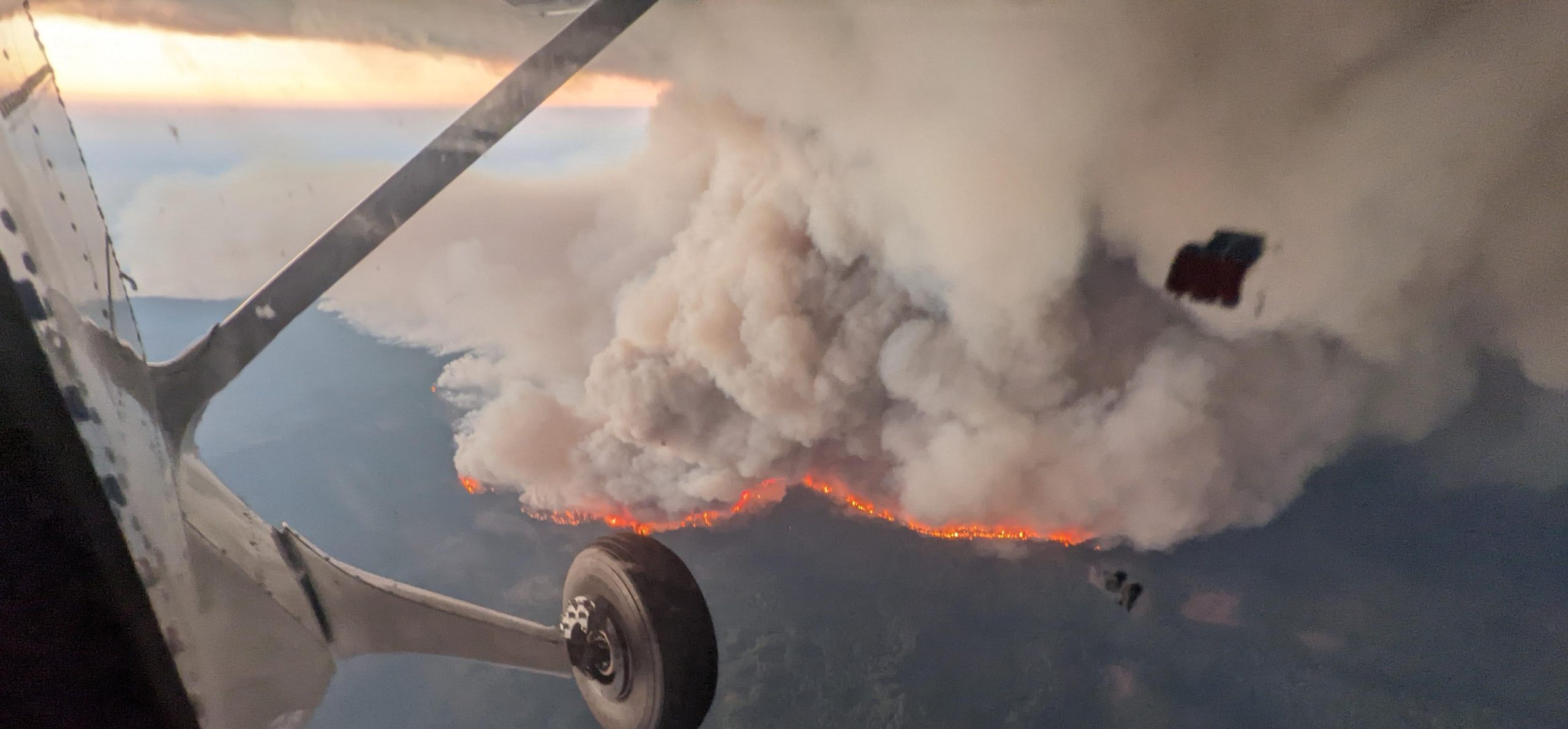
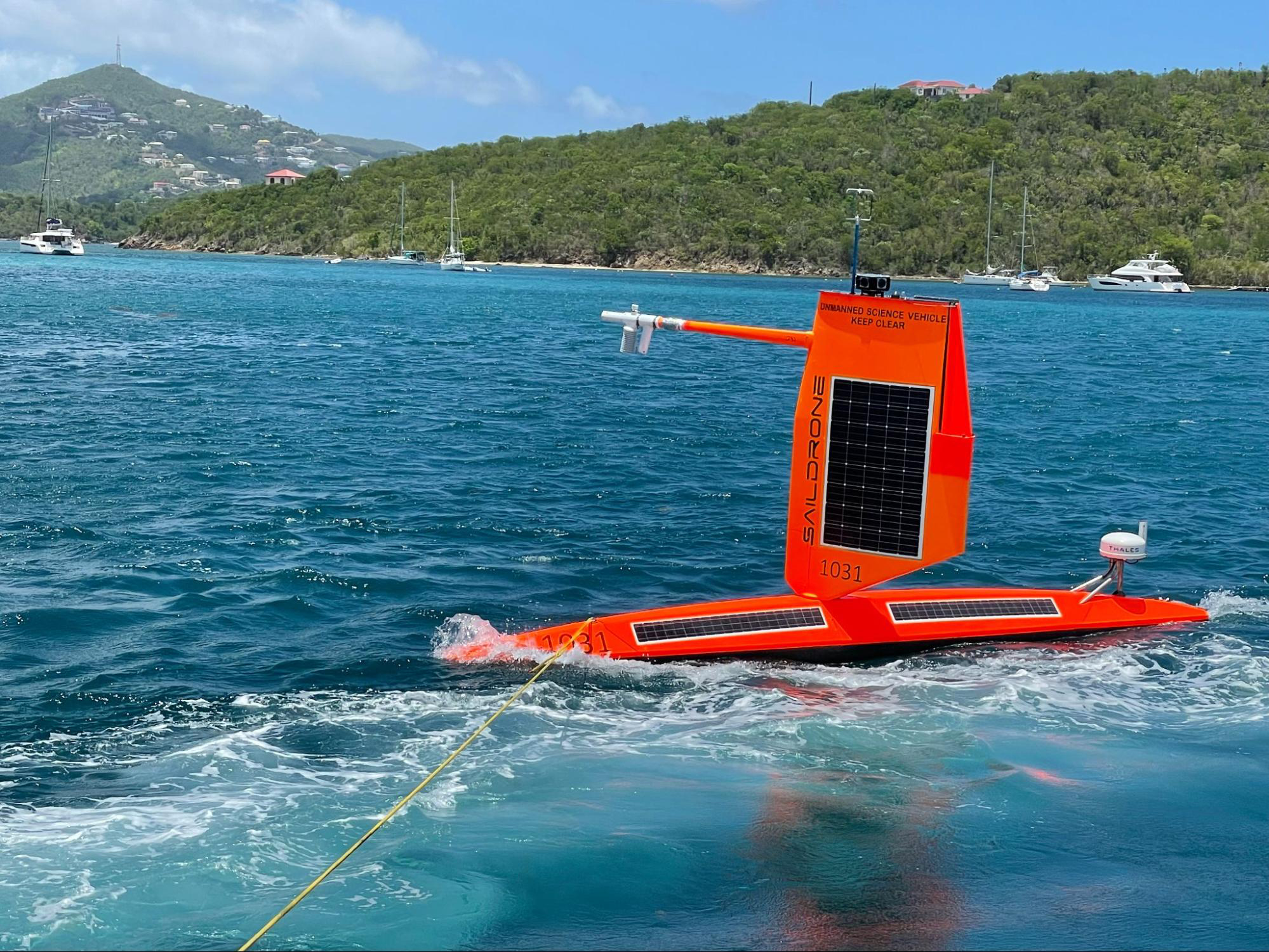
No sign of greenhouse gases increases slowing in 2023
Levels of the three most important human-caused greenhouse gases – carbon dioxide (CO2), methane and nitrous oxide – continued their steady climb during 2023, according to NOAA scientists. While the rise in the three heat-trapping gases recorded in the air samples collected by NOAA’s Global Monitoring Laboratory (GML) in 2023